GABA deficiency - what it is, how to recognize it and what to do about it
Introduction
We often talk about stress, overstimulation and burnout, but rarely about what's going on behind the scenes in your brain. One of the key players you rarely hear mentioned? GABA. A neurotransmitter that literally creates calm in your head.
Yet more and more people are struggling - without knowing it - with a GABA deficiency. They feel restless, sleep badly, get overexcited easily or have the feeling that they can never really relax. Recognizable? Chances are your GABA level is out of balance.
In this blog, we dive deep into exactly what GABA is, how a deficiency occurs, what the symptoms are and - more importantly - what you can do about it. We connect science with practice, personal experiences with solutions. So that you can regain more peace, focus and energy.
More and more organizations are looking for ways to seriously address mental wellness. Recharge360 supports companies in this with proven tools that help with relaxation, recovery and activation - exactly what GABA supports, but at the organizational level.
1. What exactly is GABA?
GABA is the abbreviation for gamma-aminobutyric acid. It sounds chemical, but it's a substance that your brain makes itself. And it's crucial to your mental balance.
What is GABA?
GABA is a neurotransmitter - a kind of messenger in your brain - that creates calm. Whereas substances like glutamate and dopamine provide activity, focus and action, GABA actually provides inhibition and relaxation. You can think of it as the brake pedal of your brain.
When GABA is functioning properly:
-
Can relax well after exertion
-
Fall asleep faster
-
Recover faster from stimuli
-
Feel less anxiety, brooding thoughts and tension
In short, GABA is essential to avoid becoming overexcited in a world that is constantly "on.
GABA action: balance between throttle and brake
Your brain works on balance. Where dopamine and glutamate throttle, GABA keeps you from overspeeding. But when that balance is disturbed - for example, by prolonged stress or lack of nutrients - then GABA release decreases.
The consequence? You stay on, even if you want to relax. Your body is tired, but your head keeps grinding. You experience sleeping problems, increased muscle tension or a constant feeling of restlessness. Exactly the complaints that many people with GABA deficiency describe.
👉 Tip: Recharge360 helps organizations bring back that balance - not with pills, but with practical behavior change and smart tools. Read more about vitality in the workplace
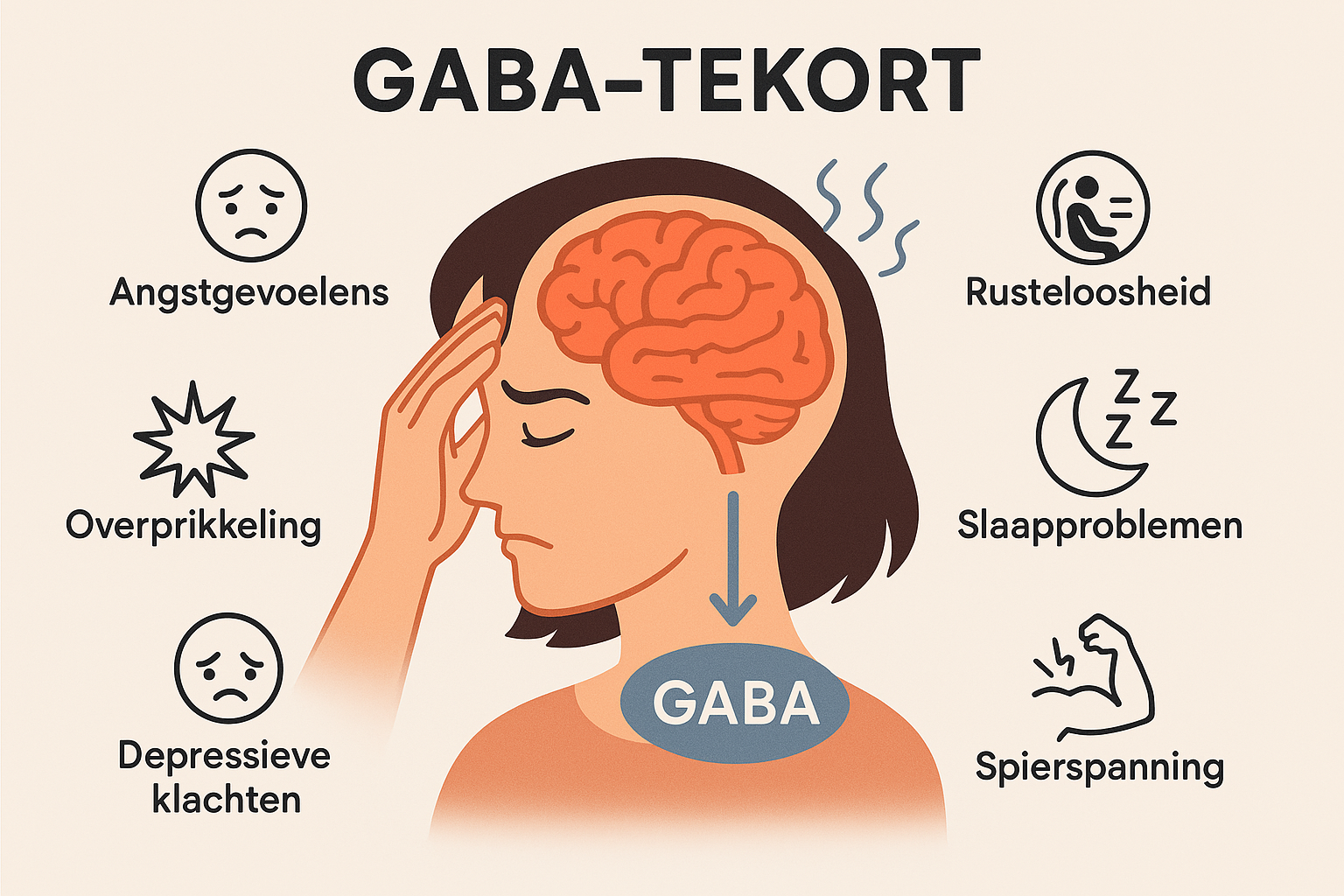
2. The symptoms of a GABA deficiency
You often don't immediately feel a GABA deficiency as "a lack of a substance," but you notice it in how you feel and function. You feel tense, more easily irritated or overexcited, and have trouble truly relaxing - even when you set aside time. The symptoms of a GABA deficiency are noticeable both physically and mentally.
GABA deficiency symptoms
Below are the most common symptoms of GABA deficiency:
🧠 Mental symptoms
-
Chronic brooding
-
Feelings of anxiety or inner turmoil
-
Difficulty sleeping or sleeping through
-
Irritability and emotional swings
-
Concentration problems
🏃♂️ Physical symptoms
-
Muscle tension (especially in neck and shoulders)
-
Tremors or vibrations
-
Accelerated heart rate or shallow breathing
-
Headache or dizziness with no apparent cause
-
Fatigue despite enough sleep
These symptoms overlap in part with those of a dopamine deficiency, which is not surprising - many neurotransmitters work together. Where dopamine is responsible for motivation and reward, GABA provides calmness. A lack of both reinforces each other.
👉 Want to replenish your dopamine deficiency? Then always start with rest and recovery - Recharge360 helps with practical routines and awareness. Read how to solve absenteeism with vital teams.
3. GABA and anxiety: what is the connection?
Many people with GABA deficiency also experience anxiety symptoms - from mild nervousness to panic attacks. This is no coincidence. GABA plays a key role in the inhibiting overactivity in your brain. If that brake is removed, fear thoughts and feelings can arise and linger more easily.
GABA anxiety experiences
Scientific research shows that people with anxiety disorders often have lower levels of GABA in their brain (Cryan & Kaupmann, 2005). Many users of GABA supplements or relaxation techniques report feeling calmer and more stable. Although the scientific support for supplements is mixed, the gaba experiences positive as part of a broader approach.
Experiences of users activating GABA through lifestyle:
-
"My head feels calmer, like there's less noise inside."
-
"I finally feel like I can relax without having to sleep."
-
"My feelings of anxiety are less intense and I react more calmly in moments of stress."
➡️ Please note: GABA supplements are not a panacea. It's all about structural approaches: exercise, breathing, sleep, nutrition and mental guidance.
👉 Recharge360 focuses precisely on these behavioral components. With tools that help calm your nervous system and become mentally stronger. Read more about emotional well-being in the workplace.
4. L-glutamine deficiency and its link to GABA
In order to make GABA, your body needs building blocks. One of the most important of these is L-glutamine - an amino acid found in your muscles, intestines and brain, among others. A l-glutamine deficiency may thus indirectly cause reduced GABA levels.
What is L-glutamine?
L-glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in your body. It is involved in muscle repair, immune function AND - important for this blog - it is a precursor to glutamate, from which your brain can then make GABA.
L-glutamine deficiency symptoms
If you get too little L-glutamine (for example, due to stress, illness, overtraining or poor nutrition), the following symptoms may occur:
-
Reduced muscle strength or muscle breakdown
-
Gastrointestinal problems (such as leaky gut)
-
Reduced concentration and brain fog
-
Getting overexcited faster
-
Increased susceptibility to infections
-
Slower recovery after physical or mental exertion
Because L-glutamine indirectly supports the production of GABA, when it is deficient you often see symptoms similar to a GABA deficiency - Think inner turmoil, poor sleep and brooding.
👉 Recharge360 often works at companies with themed weeks on nutrition and recovery. These help employees become more aware of these chains in the body, without making it complex. See how Recharge360 works on workplace vitality here.
5. Calming your nervous system: what does work?
If you are experiencing GABA deficiency-related symptoms, it is important to work on recovery of your nervous system. This does not start with medication, but with the right lifestyle. Only when there really is no other way will medication be considered - always under supervision.
Calming nervous system: natural approach
Your nervous system consists of the sympathetic (action) and parasympathetic (recovery) systems. In chronic stress, the sympathetic system is on too often, overloading your GABA system. Fortunately, you can activate the parasympathetic system - and thus GABA - through behavior.
Effective natural methods:
-
Deep breathing (slows heart rate and activates resting system)
-
Motion (e.g., hiking, biking, yoga)
-
Cold training or heat (such as saunas)
-
Sleep Optimization
-
Meditation or mindfulness
-
Adequate protein and healthy fats
Calming nervous system with medication?
In some cases, medication is used, such as benzodiazepines or GABA agonists. These can be temporarily effective, but have side effects and make your body less sensitive to its own GABA production. Therefore, it is important to always optimize lifestyle first.
👉 Recharge360 helps employees integrate that lifestyle change into their work week. Through micro-challenges, workshops and coaching, behavior change becomes attainable. Read 9 smart tips against burnout.
6. GABA and stress at work
Your brain needs rest to function properly. But what if your workday consists of continuous stimuli, rushed meetings and hardly any time to catch your breath? Then your brain is working overtime - and you feel it reflected in your GABA levels.
Stress at work lowers GABA
Prolonged work stress increases the production of stress hormones such as cortisol. These suppress the production of neurotransmitters such as GABA (Ziegler et al., 2020). That means: less brake, more chaos in your head.
Consider:
-
Not being able to relax after work
-
Sleeping badly while dead tired
-
Feeling agitated without immediate cause
-
Unexplained tension in your body
These symptoms are common in people who work in open offices, need to be constantly on call, or have no control over their workload.
👉 Also read: Why open offices are more likely to cause stress
👉 And: Do you have a healthy office?
The role of Recharge360 in stress prevention
Recharge360 sees work stress not as an individual problem, but as a systemic problem. The platform helps organizations bring moments of rest back into the work week - via, for example:
-
Quarterly vitascans
-
Coaching Modules
-
Micro-commands to activate recovery
-
Team challenges for relaxation and focus
All this without additional burden on HR, and with visible impact.
👉 See how Recharge360 helps to ill by stress prevent.
7. How to replenish GABA naturally.
Good news: you can support your GABA levels naturally. That doesn't mean taking pills every day - it involves habits that calm your nervous system and help your brain make GABA on its own.
Natural GABA boosters
1. Nutrition
Eat foods rich in magnesium, zinc, vitamin B6 and L-glutamine - these are co-factors for GABA production. Consider:
-
Dark green leafy vegetables (spinach, kale)
-
Avocados
-
Salmon, chicken, eggs
-
Fermented foods (such as kimchi or yogurt)
2. Breathing & relaxation
GABA is activated when you enter a state of rest. Techniques such as deep breathing (4-7-8), meditation and yoga increase the parasympathetic nervous system - which is directly linked to GABA release.
3. Motion
Regular, moderate exercise such as walking, cycling or swimming helps to break down stress hormones and increase GABA naturally (Streeter et al., 2010).
4. Sleep
GABA and sleep influence each other mutually. A healthy sleep rhythm enhances GABA function - and vice versa. Make sure you have a set bedtime, no screens before bed, and adequate sleep pressure during the day.
8. GABA & productivity: the forgotten ingredient
When we talk about productivity, we often think of focus, energy and output. But what we forget is that rest is as important as action. GABA plays an indispensable role in this: it allows you to recover, reset and recharge - so you can get back to work with focus.
Too little GABA = too much 'noise'
At a GABA deficiency your head is full. You start the day tired, get easily distracted and have trouble thinking clearly. Your brain no longer has a "quiet mode," so to speak. This leads to:
-
Less acuity in complex tasks
-
More errors or sloppiness
-
Longer recovery after meetings or stressful moments
-
Reduced creativity and decision-making skills
These are not luxury problems - they are direct threats to sustainable employability and job happiness.
Recharge360 and productivity through vitality
Recharge360 helps companies to not enforce productivity, but to unlock through vitality. Because a rested mind performs better. Consider:
-
Vitamins for your brain: through breathing, exercise and mental rest
-
Team challenges for focus and relaxation
-
Personal coaching for mental blocks
👉 Also read: Increase productivity with vitality
👉 And: Prevent psychological absenteeism in SMEs
As such, GABA is not a vague concept - it is a chemical foundation for good work.
9. The future of mental resilience
We live in a world in which work, technology and information are becoming increasingly rapid. And our brains? Those have not evolved for constant notifications, screens, deadlines and meetings. Mental resilience is becoming the skill of the future - and GABA plays a key role in it.
GABA and brain fitness
More and more tools and methods focus on training your brain. Not only to work smarter, but also to recover better. Think about:
-
Neurofeedback
-
AI-assisted coaching
-
Sleep and stress measurements via wearables
-
Targeted breathing exercises that fuel GABA
GABA is increasingly seen in this context as a measurable indicator of rest, recovery and flexibility of the brain.
Recharge360 as a guide in the new reality
Recharge360 capitalizes on this future by combining traditional interventions with modern technology. The app acts as a coach in your pocket, allowing employees to make small behavioral changes at the right time. No overload, but action at the right time - exactly what GABA supports.
👉 Also discover: 5 HR trends to embrace in 2025
10. FAQ: frequently asked questions about GABA deficiency
What to do about GABA deficiency?
For GABA deficiency, it is best to start with rest recovery, exercise, nutrition and targeted relaxation.
In fact, your nervous system needs repeated resting stimuli to re-generate GABA. Consider breathing exercises, walking, good sleep and foods rich in magnesium and vitamin B6. In some cases, counseling through coaching or programs such as Recharge360 can help make behavioral changes that support natural GABA production.
What are the symptoms of low GABAA?
Symptoms include anxiety, sleep problems, tense muscles, fretting and overstimulation.
GABAA receptors regulate rest in your brain. When GABA does not act sufficiently on these receptors, imbalance occurs: you find it difficult to relax, get stuck in an "on state," and become more sensitive to stress and stimuli.
How do you make more GABA?
You make more GABA by reducing stress, eating healthy and exercising regularly.
Your body makes GABA from glutamate, a process supported by sleep, relaxation and nutrients such as magnesium, L-glutamine and B6. Breathing and meditation increase GABA activity directly through your parasympathetic nervous system.
How do you test for a GABA deficiency?
GABA itself is difficult to measure directly, but signals can be seen through questionnaires or neurofeedback.
Blood or saliva tests are unreliable because GABA does not measure well through the blood-brain barrier. However, you can recognize patterns in behavior, emotions and physical symptoms. At Recharge360, for example, signals such as restlessness, fatigue and absenteeism are detected early via vitascans and surveys.
When should you take GABA?
GABA supplements are usually taken in the evening, preferably 30-60 minutes before bedtime.
The reason is that GABA calms the nervous system and can induce drowsiness. Note that oral GABA is not always absorbed well by the brain, so lifestyle modification remains the most important approach. Always consult with a physician or therapist before use.
What does GABA do in your brain?
GABA inhibits overactive brain cells and provides rest, focus and recovery.
It acts as a natural "brake" of the brain and helps prevent overstimulation. Without enough GABA, you remain "on," leading to stress, anxiety and fatigue. GABA supports balance, sleep and mental recovery.
What foods contain GABA?
GABA is mainly found in fermented products such as kimchi, yogurt, kefir, tempeh and miso.
Foods that support GABA production are also important: dark green leafy vegetables, broccoli, nuts, bananas, whole grain cereals and green tea contain building blocks for a healthy nervous system.
What mental disorders are treated with GABA?
Conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, depression and epilepsy are linked to GABA imbalance.
Treatments can include GABA agonists (such as benzodiazepines), as well as cognitive behavioral therapy, relaxation techniques and lifestyle modifications to support GABA action.
What are the symptoms of neurotransmitter deficiency?
Possible symptoms include mood swings, sleep problems, loss of concentration, fatigue and anxiety.
Because neurotransmitters work together (GABA, dopamine, serotonin, etc.), deficiency manifests itself in broad mental and physical symptoms. Balance between activating and inhibiting substances is crucial for functioning. Recharge360 helps recognize this through behavioral data and vital signs in the workplace.